CubeSat thermal modelling – Applying ESATAN-TMS for the cubesat industry
The challenge
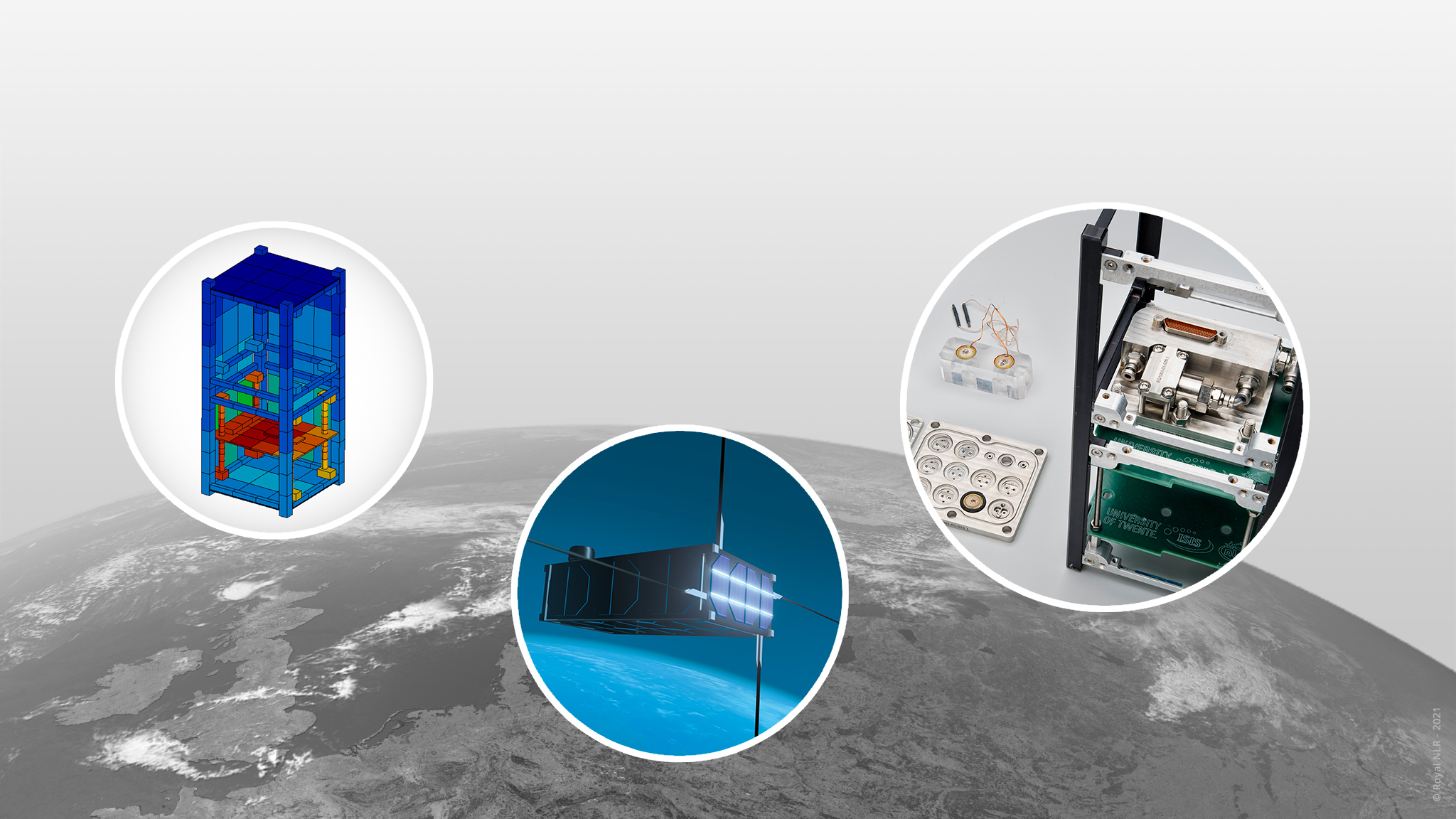
With the increase in power density, thermal control measures are needed for CubeSats. This requires low-cost hardware and software solutions, which are currently hardly available. Miniaturisation and application of thermal control systems is being worked on, however evaluating design iterations is hindered by the lack of thermal analysis imposing large uncertainties in the thermal design of CubeSats. ISIS – Innovative Solutions in Space and Royal NLR have worked together on an innovative modular approach for CubeSat thermal analyses in ESATAN-TMS. Key of this approach is the interchangeability and scalability of validated thermal submodels allowing for fast and more accurate analysis for LEO missions.
The solution
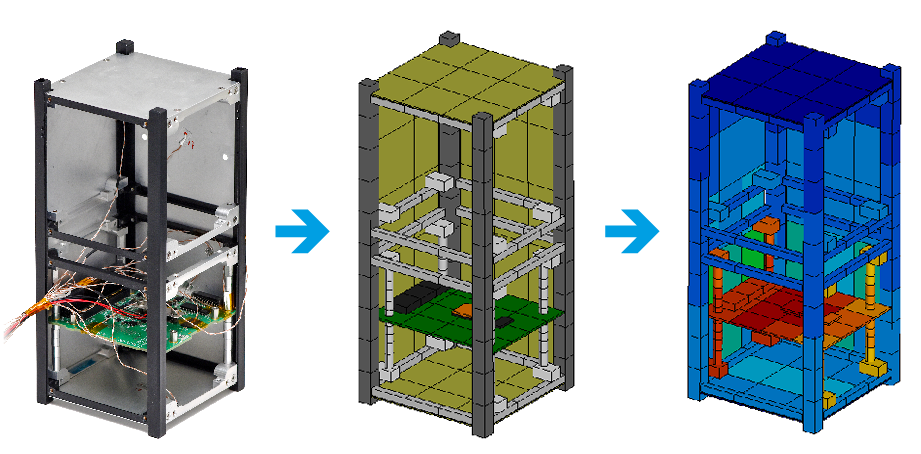
NLR’s expertise with ESATAN-TMS is applied in this project to set up a modular approach of thermal modelling of CubeSats. Thermally relevant submodels are built for commercially available subblocks, like the ISIS TXS-module, and general building blocks of a CubeSat frame. This is built in such a way, that it can be easily adapted and assembled into an entire CubeSat system. The correct modelling of interfaces between sub-models is herein critical for the thermal maturity of the model. Hence a lot of attention is given to this minor detail in the assembly. In the next stage of the project, the thermal submodules were correlated with the results of thermal vacuum tests. This correlation will ultimately result in a verified thermal model of the submodules.
What did we do?
A library of validated thermal sub-models will be created in ESATAN-TMS, allowing for fast and accurate orbital analysis, which results in improved thermal designs of CubeSats. CubeSat manufacturers and integrators can use the thermally verified submodels in ESATAN-TMS and decrease their development time of the design of a CubeSat by implementing the thermal modelling in an early stage of the design cycle. The complete panel is cured on a female mould in an autoclave at a higher temperature and pressure.
To support the stiffeners during this process no labour intensive tools were used. Instead of the common used high number of supporting blocks a silicon bag is developed. The silicon bag has the same pattern as the final panel with stiffeners. In this way, an affordable panel was made with integrated stiffeners. No man-hours are required for cleaning of tool blocks, bonding of stiffeners or the installation of fasteners to connect stiffeners
Project partners:
Industry (EU) : ISIS
Research organisations : Royal NLR
Start : 2019
Duration : no end data