Airbus predicts a demand for more than 40,000 new passenger and freighter aircraft deliveries over the next 20 years. As part of these types of ambitions aerospace manufacturers aim to recycle as much of their constituent materials as possible. But recycling at end-of-life is made more difficult by 20 to 30 years of maintenance, repair and overhaul (MRO) operations, where new (possibly polluting) replacement materials may have been added along the way.
Remanufacturing is another industrial process to contribute to more sustainable products, as it aims to reduce waste and environmental pollution. Not only is remanufacturing an environmentally friendly process, it allows products to be reused, rather than go to waste, and therefore supports a circular economy.
Resource savings
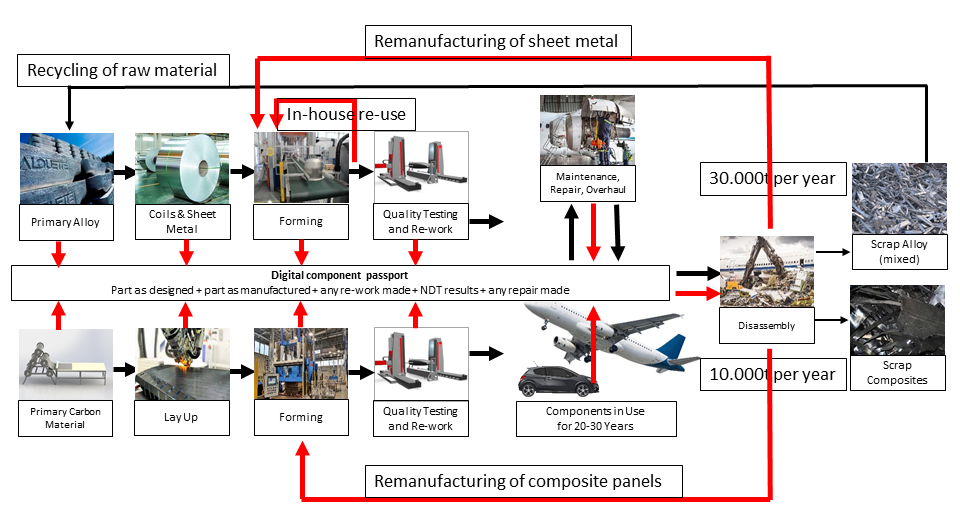
The COMPASS project aims to have a significant impact by enabling the remanufacturing of approximately 30% of the world’s aircraft-sourced sheet metal parts and thermoplastic composite panels. The remanufacturing process will make direct use of end-of-life components or production scrap from aircraft or automobiles, retaining the high value inherent in the original sheet metal and composite panels, instead of re-melting or shredding them as recycled secondary raw materials, or sending them to landfill.
The total commercial value could be on the order of €60 million per year (30,000 tonnes per year of end-of-life scrap and 14,000 tonnes per year of production scrap) for metal alloys and €500 million per year for composites (10,000 tonnes per year) worldwide by 2035. This would clearly lead to significant resource savings and promote a circular economy approach in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Digital tools
Launched in January 2024, the COMPASS project is a collaboration between 13 leading European industry and research partners, funded by the European Union’s Horizon Europe programme. The project coordinator from Austrian research company PROFACTOR said: “The digital tools developed in COMPASS will make disassembly processes efficient for extracting sheet metal or panels from decommissioned aircraft or cars, including a digital component passport. Key attributes to support remanufacturing will be captured and stored in the digital component passport for tracking component information throughout the product lifecycle. In addition, remanufacturing planning software will optimise the matching of incoming and outgoing parts for the creation of new products.”
Digital passports are pivotal elements in collecting and using data throughout the life cycle of components, supporting the remanufacturing process aimed at giving components a second life without first converting them to raw material.
As one of the COMPASS partners, NLR supports the development and application of these digital component passports (DPP, Digital Product Passport). For this NLR combines its knowledge, expertise, and technology with respect to cross-organisation secure collaboration among engineers at several parties in the aerospace sector, with the application of state-of-the-art digital technologies and concepts, including digital twinning and digital threads.
Driving Circularity
The COMPASS project addresses the growing challenge of efficiently recycling and remanufacturing components at the end of their lifespan. By employing advanced remanufacturing techniques, COMPASS will extend the life of these components, minimizing the need for raw material extraction and reducing environmental impact of new component production.
Data-Driven Approach
COMPASS introduces a novel data-driven approach to remanufacturing, leveraging digital tools and exploiting the notion of a DPP. Digital tools will streamline disassembly processes, ensuring efficient extraction of sheet metal and composite panels. The DPP will also facilitate the collection of relevant component data, facilitating improved quality control and optimization of remanufacturing operations.
Partnership for Innovation and Impact
For a duration of 3 years COMPASS will bring together a diverse consortium of experts from academia, research institutions, and industry, representing Austria, Netherlands, Spain, Italy, and Germany. This collaboration will bring together cutting-edge technologies and expertise to develop and drive innovation in remanufacturing processes.
More information
Please check out the following link for additional information about the project: https://www.compass-horizon.eu/
The COMPASS Project is co-funded by the European Commission within the Horizon Europe Programme Views, grant number 101136940. Opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.




