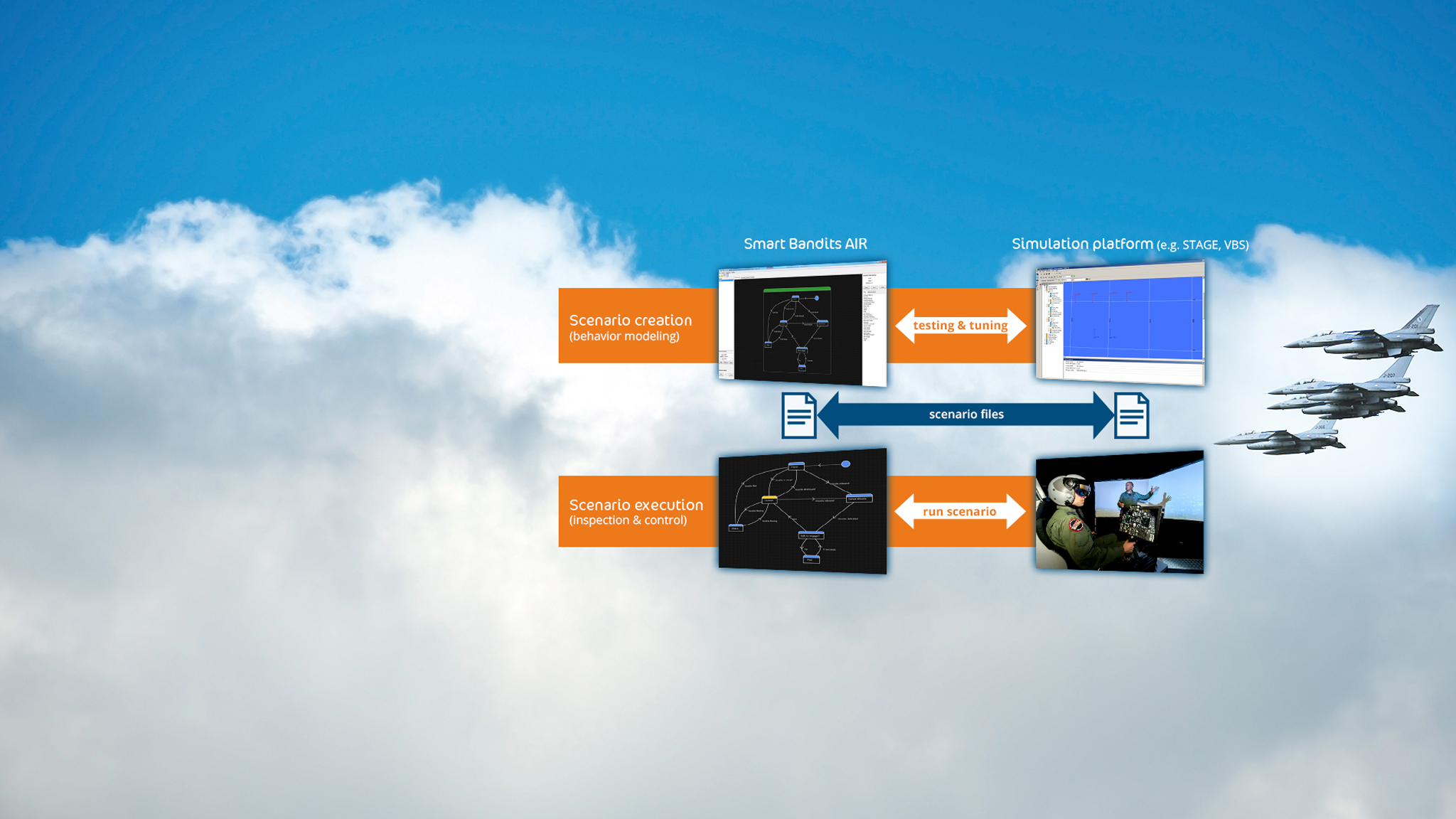
Training design
Traditionally, instructional design models have a strong focus on part task training in early phases of a learning process, but the 4C/ID model advocates a structured combination of both. The sequence of learning tasks (whole tasks) is the backbone of training, while part task practice supports learning or refreshes the highly routinised skillset at the time at which it is needed most in the sequence of learning tasks. The design of a training session is a detailed process with careful considerations. The TNA focused mainly on broad lines and high-level competencies. A training design investigates small operational details and outlines the training in the form of blueprints. At first, blueprints are designed without limitations to prevent constraints-driven training. If limitations in a new training design are too decisive, there is risk of constraints-driven training. This can potentially result in inefficient and/or ineffective training.
The design is afterwards adjusted to meet the present limitations.
A blueprint will contain:
Learning tasks within a module (whole- and part tasks)
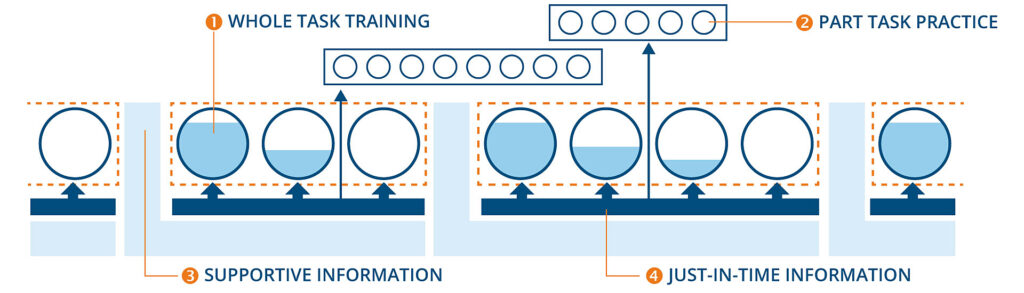
NLR uses an approach that consists of whole task learning (1) and part task practice (2). The approach uses experience-based learning, which means that learning occurs in the full context of the operation. Therefore, the learning tasks are called whole tasks. Additionally, parts of the whole tasks can be selected and practiced separately from the whole task. This promotes automation of the skill or can be an opportunity to train the competency in isolation. The blueprint presents a structure of whole tasks and part tasks, divided into modules and increasing in complexity.
Complexity factors
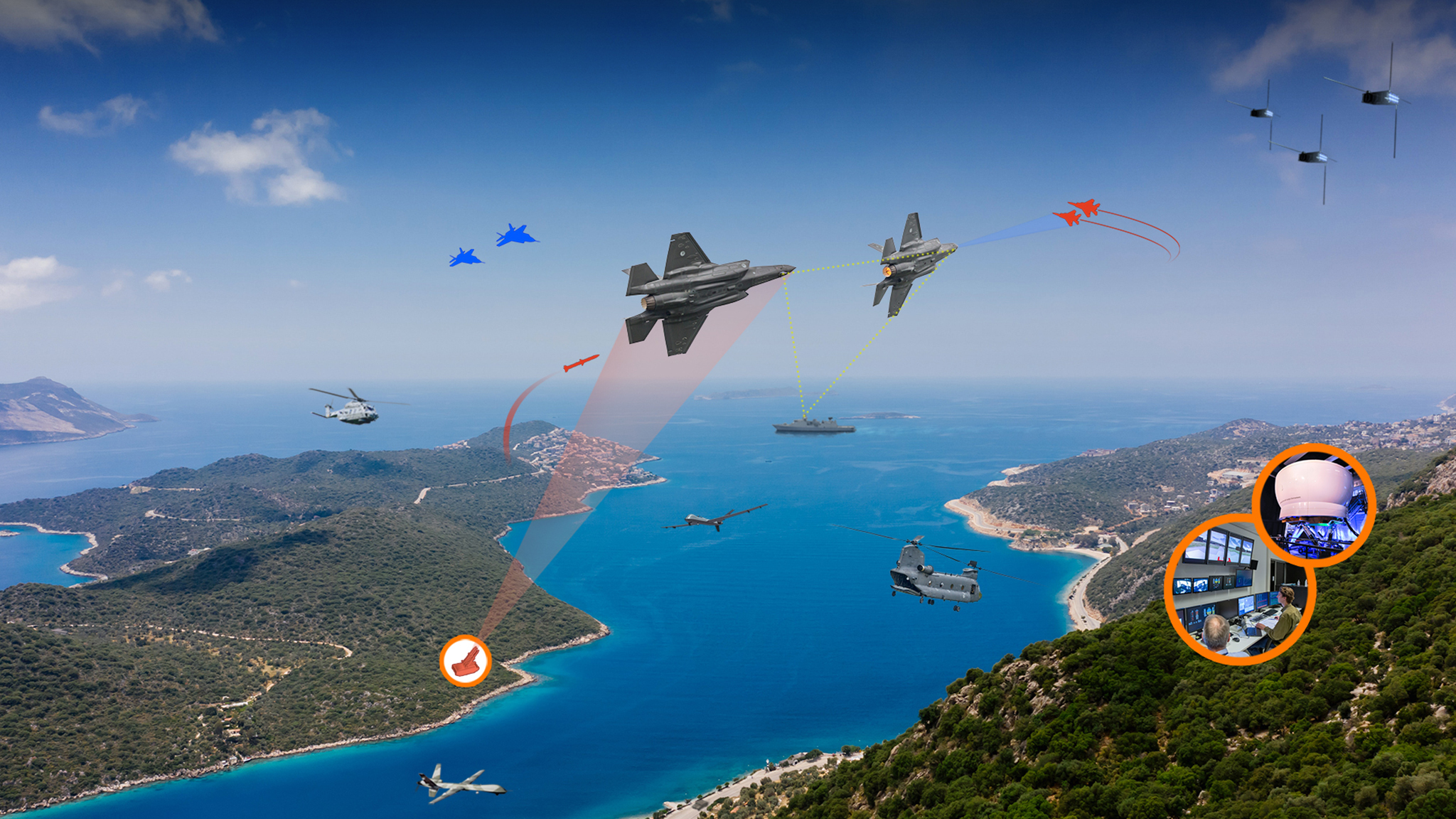
Operational conditions are translated into complexity factors, which can be used to tune the complexity of whole tasks in accordance with the progress of the trainee. The weather during flight is an example of a complexity factor. However, the weather cannot be changed. A complexity factor that is easily variable is the support of an instructor. Therefore complexity factors needs to be adjusted on each other to reach a complexity level that is suitable to the competence of the trainee.
Supporting knowledge, just-in-time knowledge and the level of instructional support
The complexity of the whole tasks increases between the modules. And within each module the level of instructor support declines (represented in blue within each whole task) .Supportive information (3) and Just-In-Time (JIT) information (4) are provided to support the whole task performance along the different scenarios. Supportive information is presented at the start of a module, which is often core information. Just-In-Time information is presented right before it is needed. This information is often very specific.




